Business Service Management
In contrast to telecoms, the corporations don't make a profit directly from operating their IT infrastructure. The IT infrastructure is a foundation of the company's business services which, in their turn, ensure efficient operation of the whole business.
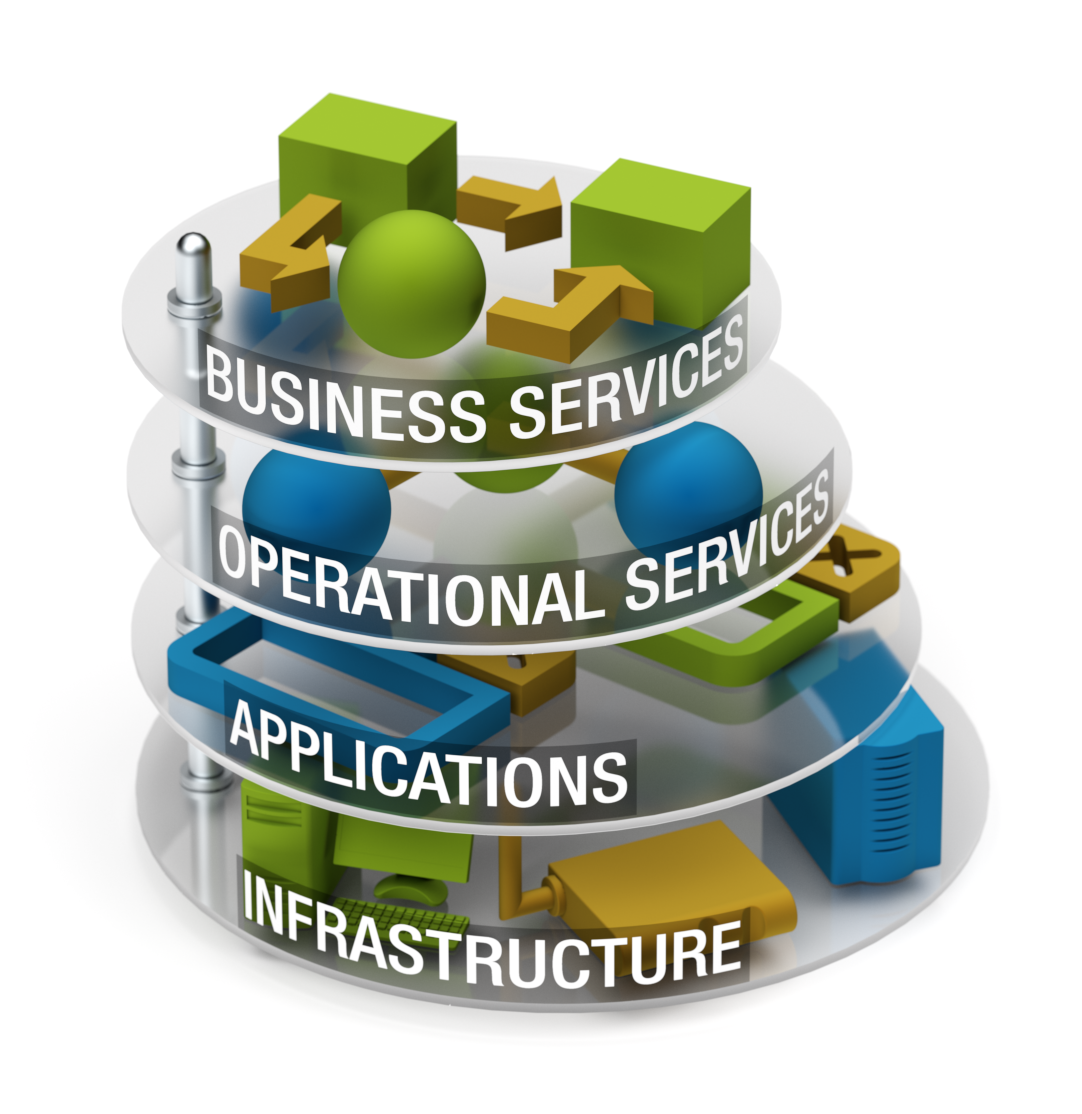
Thus, the corporate IT infrastructure monitoring and management are always multi-tiered:
| Hardware infrastructure monitoring (servers, routers, switches, printers, etc.) |
| Application monitoring (e.g., web and mail server operability monitoring) |
| Consolidated operations monitoring (e.g., cluster or web farm monitoring) |
| Business service monitoring (e.g., online ticket order process monitoring) |
Network hosts and applications running on them can be perfectly monitored using the out-of-the-box tools. Their monitoring is nothing more than proactive prediction of the negative KPI trends and reaction to the threshold violations. The list of KPIs is well-known and most hosts/applications are ready to report them via standard protocols.
Each business service is unique. It depends on many network elements (devices and applications), hence its operability is ensured by the operability of those elements. However, there is no "magic formula" describing their relations. For example, if a critical service depends on an application server cluster, a complete failure of a single application server doesn't even mean that the business service is degraded. Establishing a service by "clicking several hosts and applications" is a good marketing device, but complex real-life services require a more advanced multi-level workflow.
Most services rely on a specific multi-vendor combination of hardware and software products, making the niche monitoring products offered by their manufacturers useless or inefficient for monitoring such services as a whole.
Service Modeling
AggreGate Network Manager provides a rich set of instruments for modeling the aggregated KPIs of the most complex business services and associating those KPIs with the underlying applications and infrastructure resources:
| Wide range of device drivers for obtaining the raw data from almost any known type of data sources |
| Expression language for evaluating the custom status of network nodes and applications from their original KPIs |
| Query language for combining the information fetched from similar elements and joining the arbitrary server-side data structures for further analysis |
| Modeling engine for describing a service by custom properties, operations and events, as well as dynamically executed business rules, which link them to the pre-processed source data and each other. |
Once a business service modeling is finished, the rest of AggreGate's data processing and visualization tools (such as alerts, reports or dashboards) can be used for reacting to the service model changes and monitoring in real-time. The model events will be processed in the same way as ordinary network events, the service performance statistics will be preserved, and its status can be visualized by designing custom widgets in the AggreGate's unique UI Builder.
Business service models ensure a deep understanding of the underlying IT resources' impact on the service level, allowing to achieve a continuous service quality improvement.
SLA Monitoring
In addition, remaining highly available, most business services should also meet the custom Service Level Agreements (SLAs). Those SLAs are often contracted and their violation can lead to huge reputational and financial losses.
The status and performance indicators of a service modeled inside AggreGate Network Manager can be accompanied by their operational level and service level requirements, allowing to:
| Immediately react to the sudden SLA breaches by notifying system operators | Plan the capacity of underlying resources to ensure long-term service level compliance |
| Evaluate the impact of IT infrastructure failures on business processes | Predict the SLA violation dates and inform system administrators in advance |
| Collect the SLA compliance statistics for further reporting | Identify the migration, consolidation and license reduction opportunities |
| Visualize the availability and quality of business services |